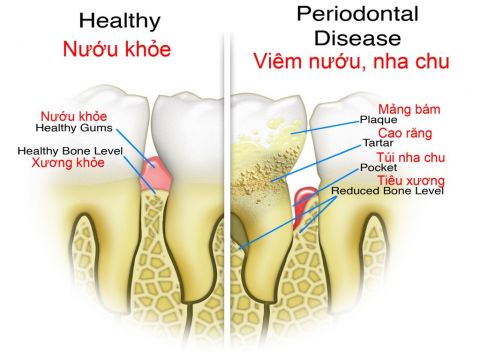
Gum disease, also known as periodontal disease, is an infection of the tissues that support the teeth. It is caused by the buildup of plaque, a sticky film of bacteria that forms on the teeth. If plaque is not removed through regular brushing and flossing, it can harden into tartar, which can only be removed by a dentist or dental hygienist.
There are two main stages of gum disease: gingivitis and periodontitis.
- Gingivitis: This is the early stage of gum disease, characterized by red, swollen, and bleeding gums. At this stage, the infection is limited to the gums and can often be reversed with proper oral hygiene and regular dental check-ups.
- Periodontitis: This is the advanced stage of gum disease, characterized by the inflammation and infection of the gums, the bones supporting the teeth, and the connective tissues. At this stage, the infection can lead to the loss of teeth, receding gums, and bone deterioration. Treatment at this stage may include scaling and root planing (deep cleaning), antibiotics and surgery.
Cause of periodontal disease
The main cause of periodontal disease is poor oral hygiene, which allows plaque to build up on the teeth and gums. The bacteria in plaque release toxins that irritate the gums, causing them to become red, swollen, and bleed easily.
However, there are several other factors that can contribute to the development of periodontal disease, including:
- Poor nutrition: A diet high in sugar and refined carbohydrates can increase the risk of periodontal disease, as it can lead to plaque build-up and tooth decay.
- Hormonal changes: Hormonal fluctuations during pregnancy, menopause, or taking certain medications can make gums more sensitive and susceptible to infection.
- Tobacco use: Smoking or using other forms of tobacco can increase the risk of gum disease, as it can make it harder for the gums to fight off infection and can impede the healing process.
- Medical conditions: Some medical conditions, such as diabetes and heart disease, can increase the risk of periodontal disease.
- Genetics: Some people may be more susceptible to periodontal disease due to their genetics.
- Medications: Some medications can cause dry mouth, which can lead to an increase in plaque and bacteria.
Complications
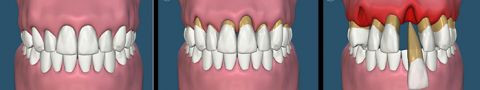
If left untreated, gum disease can lead to a variety of complications, both for the oral health and the overall health.
- Tooth loss: Periodontal disease can cause the gums to pull away from the teeth, creating pockets that can become infected. As the disease progresses, the bone and connective tissue that hold the teeth in place can be destroyed, leading to tooth loss.
- Receding gums: As the gums pull away from the teeth, the roots of the teeth become exposed, making them more susceptible to decay and infection.
- Bone loss: Periodontal disease can cause the bone that supports the teeth to deteriorate, leading to loose teeth and an increased risk of tooth loss.
- Bad breath: The bacteria associated with periodontal disease can cause bad breath and a foul taste in the mouth.
- Changes in bite: As the disease progresses, the teeth can shift, change position, or become loose, which can affect the bite and cause jaw pain or headaches.
- Increased risk of other health problems: Periodontal disease has been linked to an increased risk of other health problems such as diabetes, heart disease, stroke, and respiratory disease.
- Pregnancy complications: Pregnant women with gum disease may be at a higher risk of having a premature or low-birth-weight baby.
How to prevent gum disease
There are several steps that can be taken to prevent gum disease, including:
- Brush and floss daily: Brushing twice a day and flossing once a day can help remove plaque and bacteria from the teeth and gums. It’s important to use a toothbrush with soft bristles and to brush gently along the gumline.
- Use an antiseptic mouthwash: Using an antiseptic mouthwash can help reduce plaque and bacteria in areas that are difficult to reach with a toothbrush and floss.
- Eat a healthy diet: A diet high in fruits, vegetables, and whole grains can help promote oral health and reduce the risk of gum disease. It’s important to limit sugary and acidic foods and drinks.
- Stop smoking: Smoking or using other forms of tobacco can increase the risk of gum disease, as it can make it harder for the gums to fight off infection and can impede the healing process.
- Manage stress: Stress can have a negative effect on overall health, including oral health. It’s important to manage stress through exercise, relaxation techniques, or other methods.
- Visit the dentist regularly: It’s important to visit the dentist regularly for check-ups and cleanings to detect and treat any potential issues early on.
- Maintain good overall health: Managing medical conditions such as diabetes and maintaining a healthy weight can help improve oral health and reduce the risk of gum disease.
By taking these steps and maintaining good oral hygiene, you can greatly reduce the risk of developing gum disease and keep your teeth and gums healthy.

